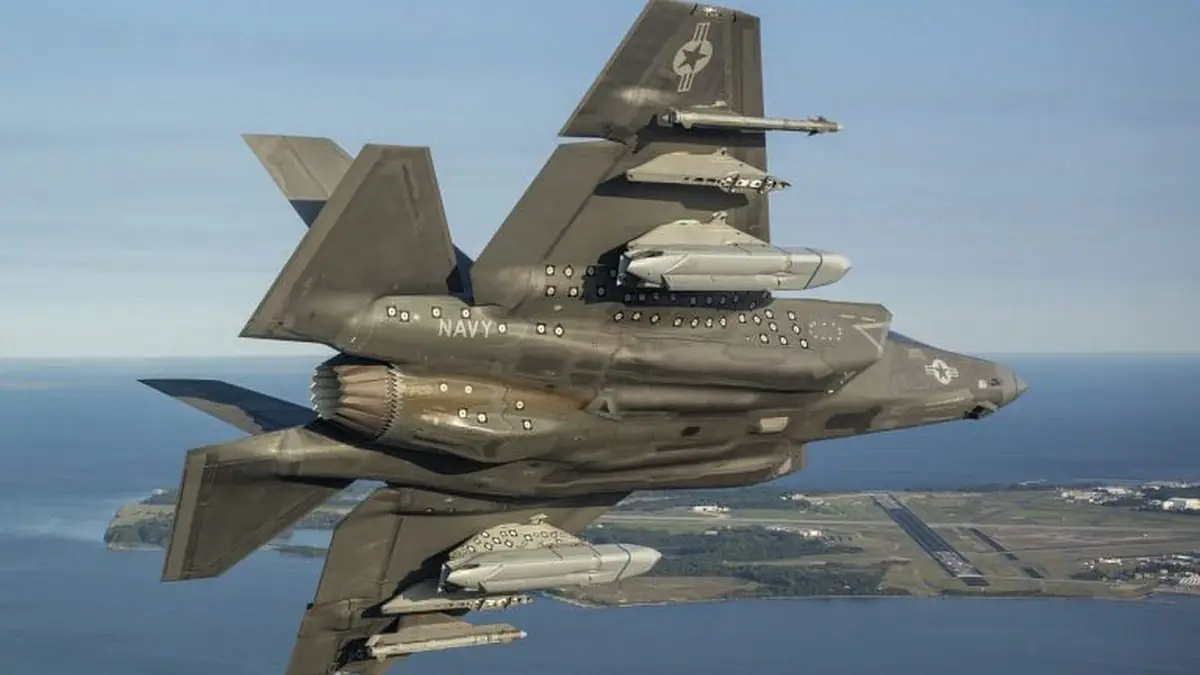
The U.S. Navy has begun testing LRASM anti-ship weapons on the F-35 fighter jet, with initial test flights conducted in early September to assess the integration of the weapon with the airframe.
The U.S. military has released the first images of the long-range anti-ship missile AGM-158C (LRASM) being carried in flight by an F-35C test aircraft from Naval Air Station Patuxent River, Maryland. The two flights, captured in photos on September 9 and 10, 2024, mark the start of testing this weapon on the F-35C.
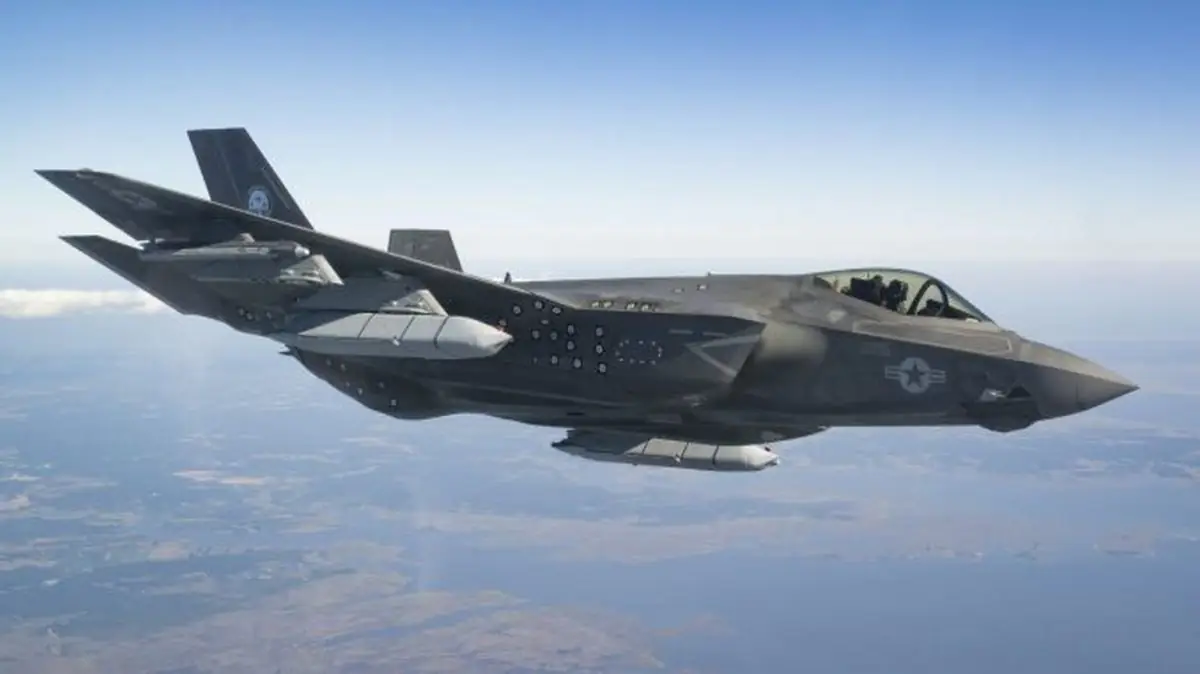

The initial test flights, part of integration efforts conducted by the Pax River F-35 Integrated Test Force (Pax ITF), revealed the F-35 carrying two LRASM missiles externally on its internal hardpoints, along with two inert AIM-9X missiles on the wing tips. Notably, this is the first time the LRASM has been seen with the same white paint as the JASSM, from which it is derived, rather than the usual black seen in previous photos.
These tests aim to assess the impact of the weapon on the aircraft’s airframe under various flight conditions and parameters, as well as to ensure the structural integrity of both systems. This is the first phase of flight tests before moving on to in-flight drop tests to evaluate weapon separation behavior, followed by full weapon testing to validate the entire engagement profile.
The anti-ship capability is critical in the context of a potential conflict with China in the Pacific, where PLA Navy (PLAN) warships would serve as primary combat assets and targets for U.S. and allied forces. The LRASM demonstrated its effectiveness in a “historic” test on April 3, in collaboration with its developer, Lockheed Martin, and the U.S. Navy. During this test, four missiles were “simultaneously in flight,” as reported by *The War Zone*. The four LRASM missiles were launched by a pair of F/A-18E/F Super Hornets, showcasing the missile’s operational readiness and coordination.

The caption accompanying the photos notes that earlier this month, Pax ITF conducted two days of test flights as part of ongoing efforts to certify the F-35C for carrying the LRASM missile. The first two flights allowed the evaluation of flutter, loads, and flight characteristics with two AGM-158s mounted on the external stations, according to the caption. Both missiles in the photos feature a blue band at the front, indicating that they are inert variants.
Pax River ITF is responsible for planning, coordinating, and executing safe, reliable, and effective flight tests for the F-35B and C variants. They also provide essential and timely data to support the verification/certification of the program and meet the operational requirements of the fleet.
In addition to verifying the impact on flight characteristics during transport and electronic launch, confirming the connection between fire control systems and missile ejection from hardpoints, these tests may also develop or provide data on specific launch parameters to achieve optimal missile performance.
The AGM-158C LRASM is the anti-ship variant of the AGM-158 Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missile (JASSM). It is designed for use on both the F-35B short takeoff and vertical landing (STOVL) fighters operated by the U.S. Marine Corps, as well as the carrier-based F-35C and F/A-18 Super Hornet, which are launched via catapult.
As shown in the photographs, the LRASM is carried externally on the wing hardpoints of the F-35C because it is too large to fit into the aircraft’s internal weapons bays. This size limitation also presents a similar challenge for the F-35B, which has smaller internal compartments for weapons.
The original JASSM (AGM-158) comes in several variants, including the now-discontinued baseline AGM-158A JASSM. The AGM-158B JASSM-ER is the extended-range version, with its variants AGM-158B-2 and AGM-158B-3 featuring upgraded electronics, guidance systems, navigation, and targeting technologies.
According to *The War Zone*, the AGM-158D JASSM-ER includes a Weapon Data Link (WDL) feature, which allows for the missile to be retargeted or reprogrammed mid-flight. This capability was referenced in the U.S. Air Force’s budget documents for fiscal year 2025 and is still under development.
Similar to the LRASM on the F-35C, the F-35A is also unable to carry the AGM-158A JASSM internally. Due to this limitation, the U.S. has opted to purchase the Joint Strike Missile (JSM) from Norway’s Kongsberg Defence and Aerospace (KDA) under a $141 million contract announced on May 31, 2024. The JSM, a land-based version of the Naval Strike Missile (NSM), is compatible with the internal weapons bays of the F-35, offering a solution for stealth missions where internal carriage is crucial for minimizing radar cross-section.

With the emergence of a maritime theater in the western Pacific, facing China, the U.S. Navy will likely need to deliver substantial strikes against the People’s Liberation Army Navy (PLAN) vessels, or at least target one or more surface ships, to gain local naval superiority. Missiles capable of altering direction and flight trajectory at unpredictable intervals to evade Chinese air defense systems would be invaluable and particularly lethal when launched in coordinated salvos. This capability would increase the effectiveness of U.S. forces in neutralizing key naval assets, complicating China’s defensive efforts and enhancing the strategic advantage in contested waters.
After launch, the LRASM navigates to its initial point using GPS guidance and employs onboard sensors for localization, identification, and final targeting. Its semi-autonomous guidance algorithms enable it to utilize less precise target data to accurately pinpoint specific targets in contested areas. This capability enhances the missile’s effectiveness in dynamic environments, allowing it to adapt to changing conditions and engage high-value targets with precision, even in the presence of countermeasures or disrupted communication links.
Source: TheAviationist








